Knowledge and Innovation Agenda Mission-Driven Innovation
Action perspective for tackling social issues and transitions
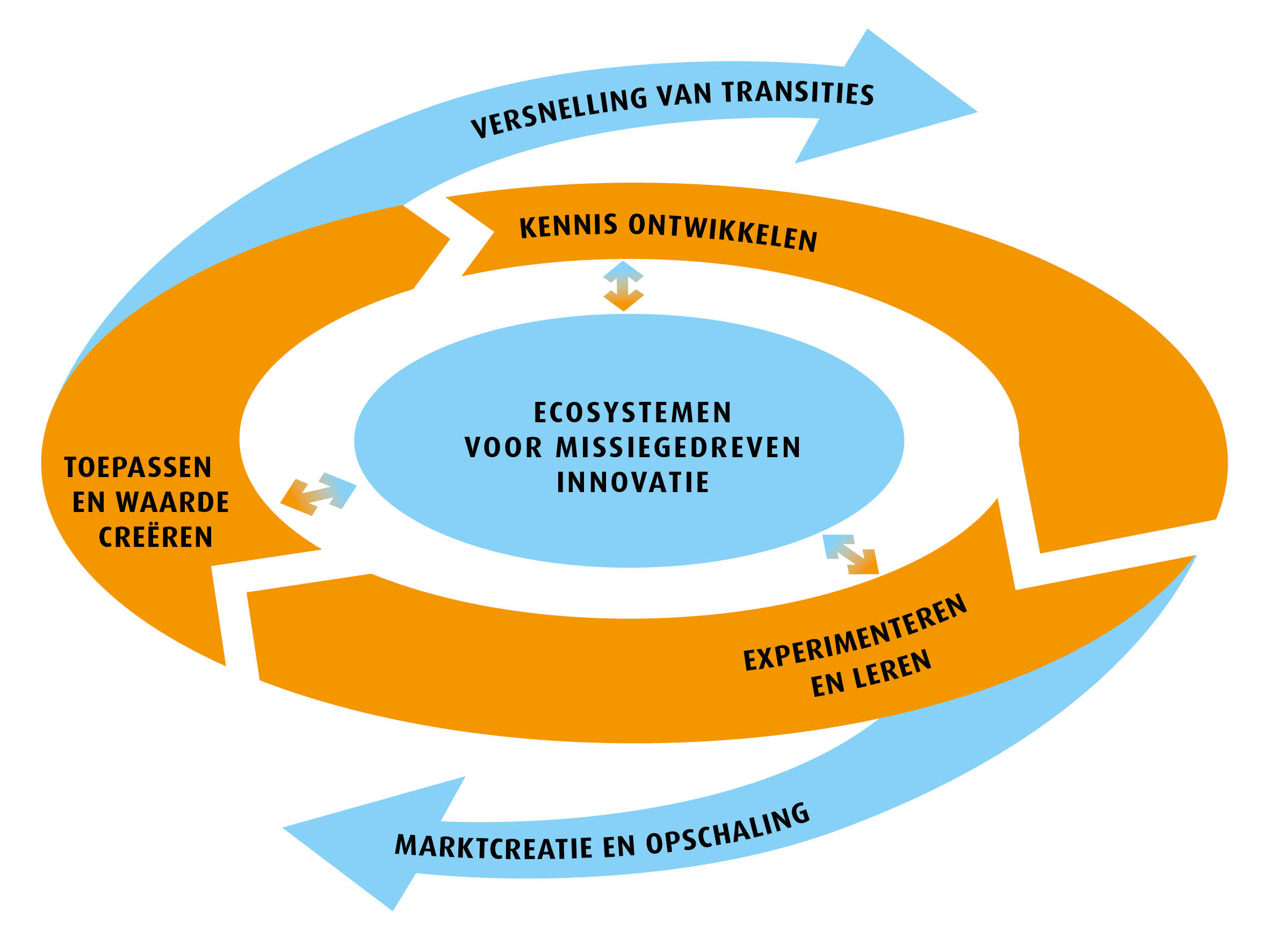
Public and private parties face major tasks to drive social issues and transitions. Never before has the world been so complex. This calls for new approaches.
The Knowledge and Innovation Agenda Mission Driven Innovation (KIA MV) offers prospects for action by developing knowledge, insights and tools. This is how we arrive at today's economic earning capacity and tomorrow's social impact.
Curious to find out what happened with KIA MV during 2025, and what 2026 will bring? Read on